Prefab homes are built off-site in sections, while modular homes are a specific type of prefab constructed in large factory-made modules and assembled on a permanent foundation to meet the same local building codes as traditional stick-built houses.
Key Differences Between Prefab and Modular Homes Explained
Prefab is a broad term for homes with major parts built in a factory, including modular, panel-built, and manufactured types.
Modular homes are a subset, built in large modules and assembled on-site to meet local building codes. Key distinctions to know:
- Prefab: Factory-built panels or smaller sections; quality and code standards vary.
- Modular: Fully built modules with wiring, plumbing, and finishes; meets same codes as stick-built.
- Manufactured: Built to HUD code, often movable, not the same as modular.
- Site adaptability: Prefab can handle narrow or remote access more easily.
- Durability: Modular often excels in strength and weather resistance.
Understanding these differences helps you choose the option that fits your priorities, whether it’s design flexibility, code compliance, or resilience in storm-prone areas.
Once you know the basics, the real value comes from seeing how these two options compare in cost, durability, efficiency, and design potential, so you can match your choice to your lifestyle and long-term plans.
Understanding the Difference Between Prefab and Modular Homes
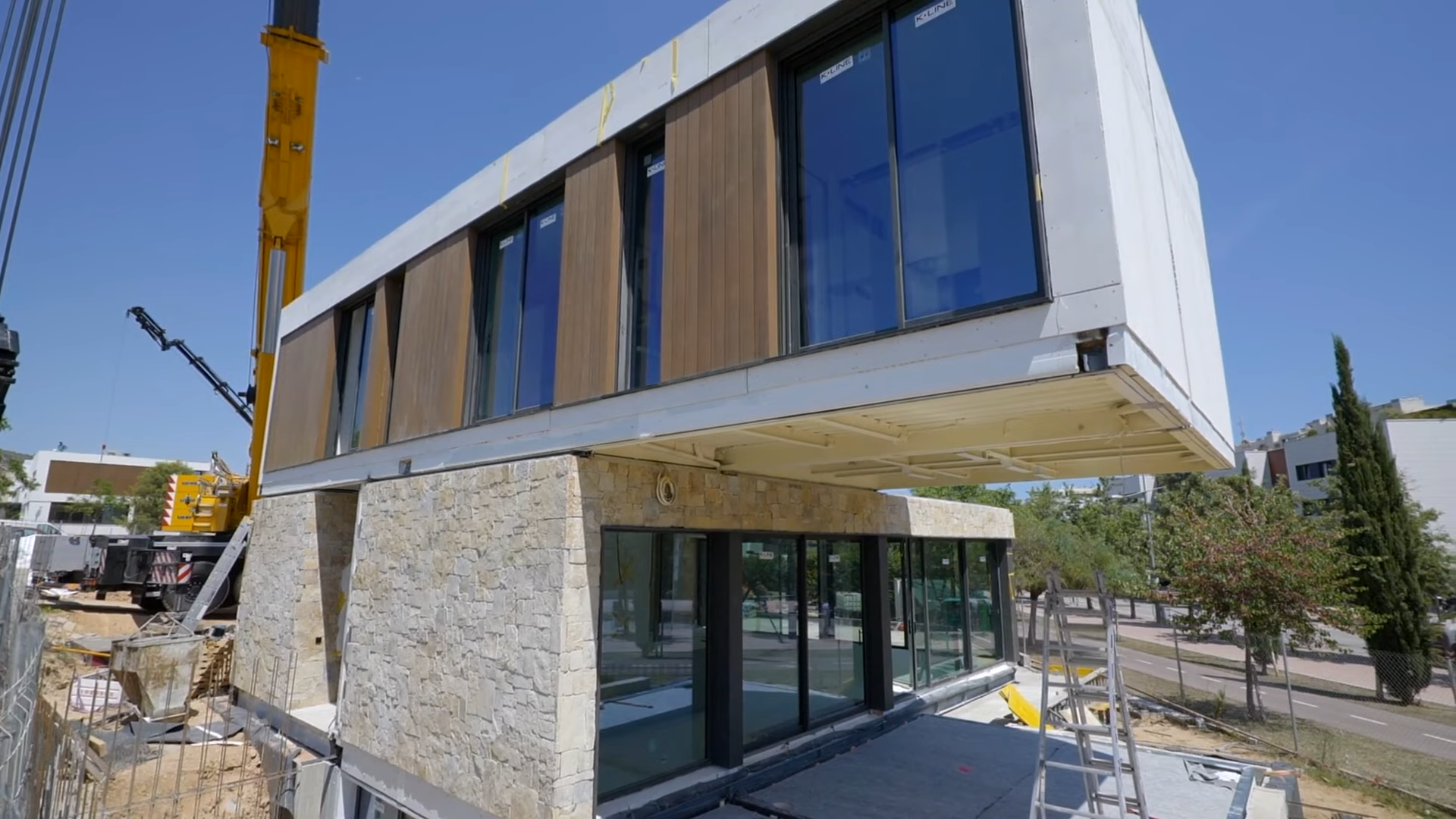

Alternative home construction offers many options, and “prefab” and “modular” are often confused. They are related but distinct, and understanding the difference is key to making the right choice.
Prefab Homes – The Broad Category
Prefabricated homes is an umbrella term for any structure with major components built off-site in a factory.
This includes modular homes, panel-built systems, and manufactured homes, covering everything from luxury houses to portable classrooms.
Modular Homes – A Specialized Type of Prefab
Modular homes are built in large, factory-made sections called modules, then transported to the site and assembled on a permanent foundation.
They meet the same local building codes and inspections as stick-built homes, offering permanence and consistency.
In some regions, such as parts of Canada, terms can overlap, adding to the confusion. One point is certain, modular and prefab homes are not mobile homes.
With these definitions clear, we can now compare their strengths across the factors that matter most.
Helpful Resource → Buying a Prefab Home | Hidden Costs & Mistakes To Avoid!
The 10-Factor Face-Off Between Prefab and Modular
Every homebuyer’s priorities are different. Some focus on speed, others on design freedom or long-term durability.
Before we break down each factor in detail, here’s a quick side-by-side comparison to give you the big picture at a glance.
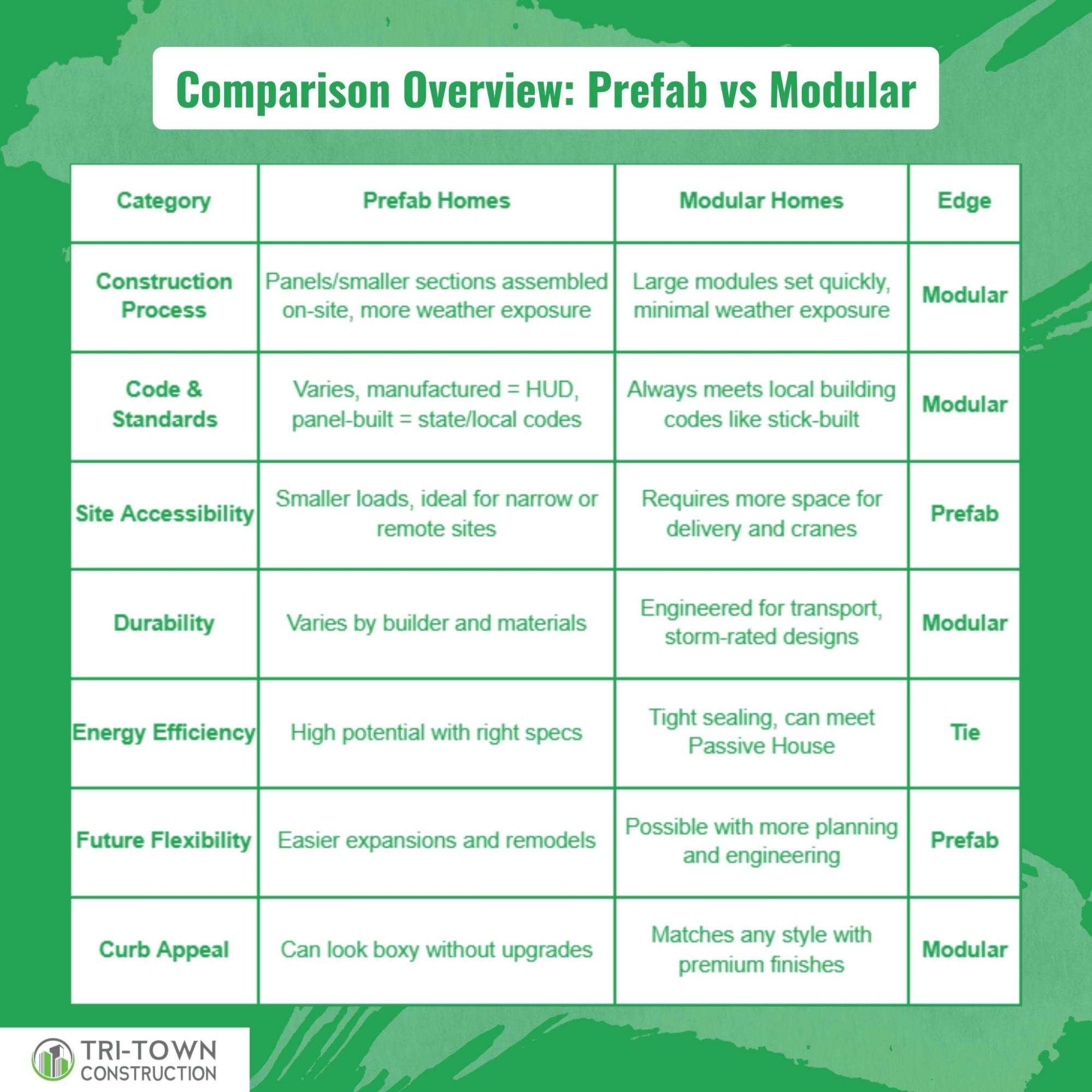
Now let’s go deeper into each of these factors to see why the scores fall the way they do and how they might apply to your own project.
1. Build Process and Site Exposure
How a home is built and how much of that process happens outdoors can make a big difference in timing and quality.
Prefab Homes: Built in panels or smaller pre-made sections that are shipped to the site and assembled piece by piece.
This approach allows flexibility in transportation and can work for a variety of site conditions.
However, more construction is completed in the open air, which means materials and workers may face delays or damage from weather.
Modular Homes: Constructed in large modules inside a climate-controlled factory. These modules leave the factory nearly complete, with wiring, plumbing, and finishes in place.
Once delivered, they are set onto the foundation with cranes, reducing time exposed to outdoor conditions.
This process shortens the construction timeline and improves quality control.
Winner: Modular – less weather risk and faster assembly make it more predictable.
2. Code Compliance and Legal Standards
View this post on Instagram
Local building codes are there to ensure safety, durability, and quality. How each construction type meets these rules can affect approvals and resale.
Prefab Homes: Code compliance varies. Manufactured homes are built to federal HUD standards, which may differ from local requirements.
Panel-built homes often meet local codes, but standards can vary from state to state, requiring additional inspections or modifications before approval.
Modular Homes: Always built to meet the same local building codes as traditional stick-built homes.
This means they must pass the same inspections and use similar materials, providing assurance to both buyers and local authorities.
The consistent code compliance also helps streamline the permitting process.
Winner: Modular – uniform code adherence simplifies permitting and inspections.
Helpful Resource → What’s Included in the Price of a Modular Home?
3. Adaptability to Remote or Challenging Sites
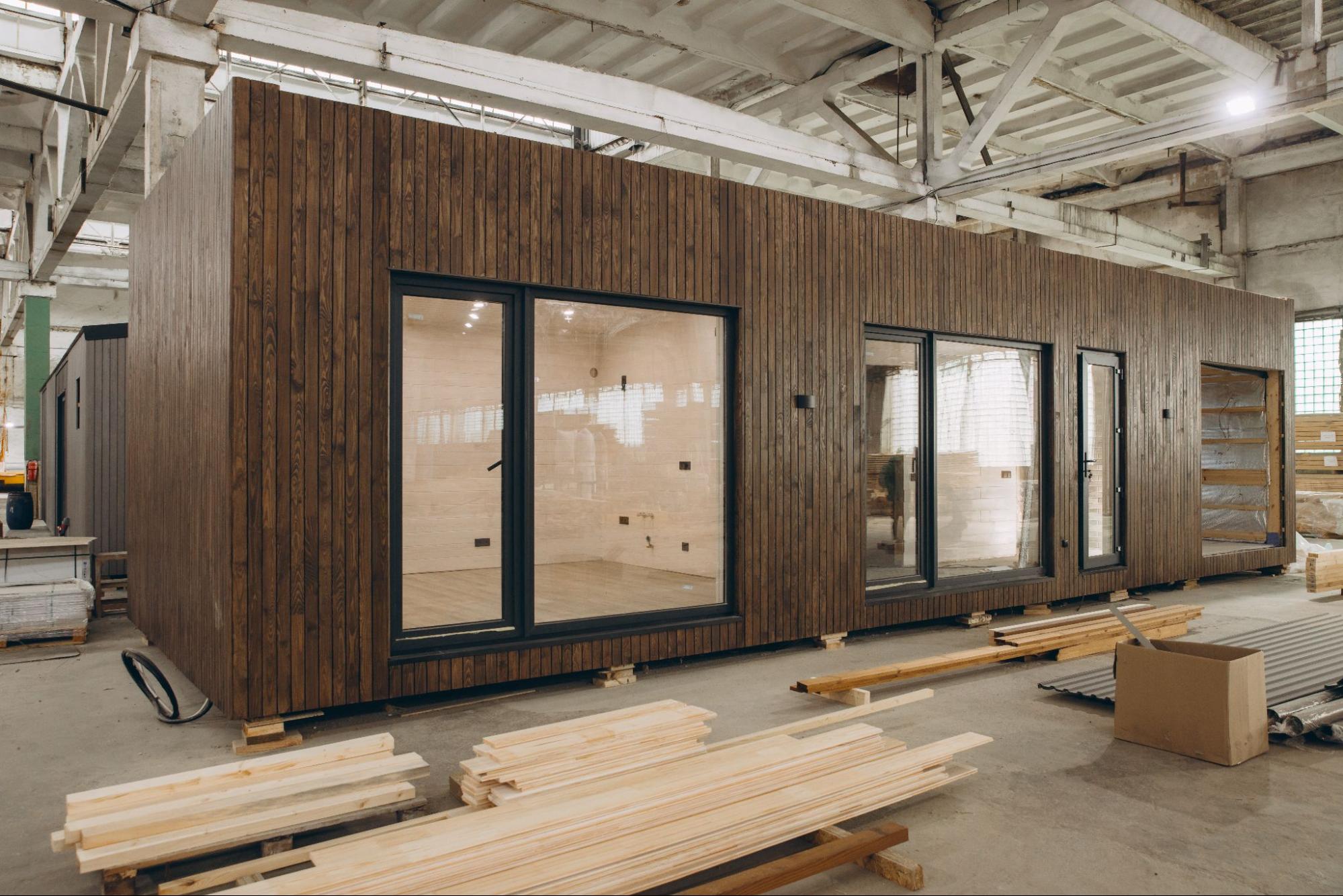

Not every lot is easy to reach. The type of construction can affect how easily your home can be delivered and assembled.
Prefab Homes: Panels and smaller sections can be transported in standard trucks, making it easier to navigate narrow roads, steep driveways, or remote rural areas.
This flexibility can reduce costs associated with special transport equipment and minimize disruption to the surrounding environment.
Modular Homes: Delivered as large, pre-finished modules that require significant clearance for trucks and cranes.
While this can limit access in some locations, experienced modular crews can still reach many challenging sites with careful planning, route preparation, and specialized equipment.
Winner: Prefab – but modular can compete closely when planned with experienced logistics teams.
4. Durability and Weather Resistance
View this post on Instagram
How well a home stands up to the elements over decades is a major consideration, especially in storm-prone areas.
Prefab Homes: Durability varies widely depending on the builder, materials, and type of prefab.
Panel-built homes can be sturdy, but some budget-friendly options may use lighter framing or materials that are less suited for extreme wind or heavy snow loads.
In severe weather zones, additional reinforcement may be required to meet local standards.
Modular Homes: Built to meet or exceed local building codes, often with added engineering to handle transport stresses.
Many modular homes are designed for hurricane zones and can withstand wind speeds of up to 180 mph.
Because they are built in sections that must survive transportation, the structural integrity is often stronger than comparable site-built homes.
Winner: Modular – its factory engineering and storm-ready designs make it the better choice for long-term resilience.
5. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability (Tie)

Energy efficiency affects both environmental impact and monthly utility bills.
Prefab Homes: Factory construction allows for precise material use and less waste.
Panelized systems can be insulated to high standards, and many manufacturers offer eco-friendly options like recycled materials or energy-saving windows.
However, performance depends on the builder’s specifications and the quality of on-site assembly.
Modular Homes: Modules are built in climate-controlled environments, which ensures insulation and air-sealing are done without weather interruptions.
This tight construction can lead to very low heating and cooling costs, and many modular designs can meet or exceed Passive House standards when specified.
Winner: Tie – both can deliver top-tier energy performance when built with the right specifications.
6. Ease of Expanding or Renovating Later
Many homeowners want the option to add space or remodel in the future.
Prefab Homes: Panel-built structures can be easier to modify because walls and roof sections are often constructed with flexibility in mind.
Adding a new room or altering layouts can be less complex and less expensive, especially if the builder planned for future expansion.
Modular Homes: Expansions are possible but can require more structural engineering to integrate seamlessly with the existing modules.
This can increase costs and complexity, although some modular designs include planned expansion points for easier future work.
Winner: Prefab – but modular homes can be just as adaptable if expansion is planned during the initial design.
7. Speed to Occupancy
View this post on Instagram
How quickly you can move in can be critical, especially after relocation or disaster recovery.
Prefab Homes: Faster than traditional stick-built houses because large parts are pre-made.
However, panel-built systems still require significant on-site work, such as weatherproofing, finishing, and utility connections, which can add weeks to the schedule if weather or labor delays occur.
Modular Homes: Built in large, pre-finished modules in a factory while site work, like foundation preparation, happens at the same time.
Once modules are delivered, assembly is rapid, and finishing touches can be completed in a matter of days, allowing move-in in a much shorter timeframe.
Winner: Modular – its parallel construction process and minimal on-site build time make it the fastest option.
8. Environmental Impact of Construction Process (Prefab win #3)
The building process itself leaves a footprint, and how each method manages resources matters.
Prefab Homes: Panels are shipped in smaller loads, which can reduce transport emissions compared to hauling large modules.
The factory build process also minimizes on-site waste, and some manufacturers source materials locally to reduce the carbon footprint even further.
Modular Homes: Requires fewer deliveries overall and maximizes material efficiency in the factory, but larger transport loads may mean higher fuel use per trip.
Many modular builders also use sustainable materials and recycling programs to offset environmental impact.
Winner: Prefab – but the difference is slight, and modular homes can be equally eco-conscious depending on logistics and sourcing.
9. Aesthetics and Curb Appeal
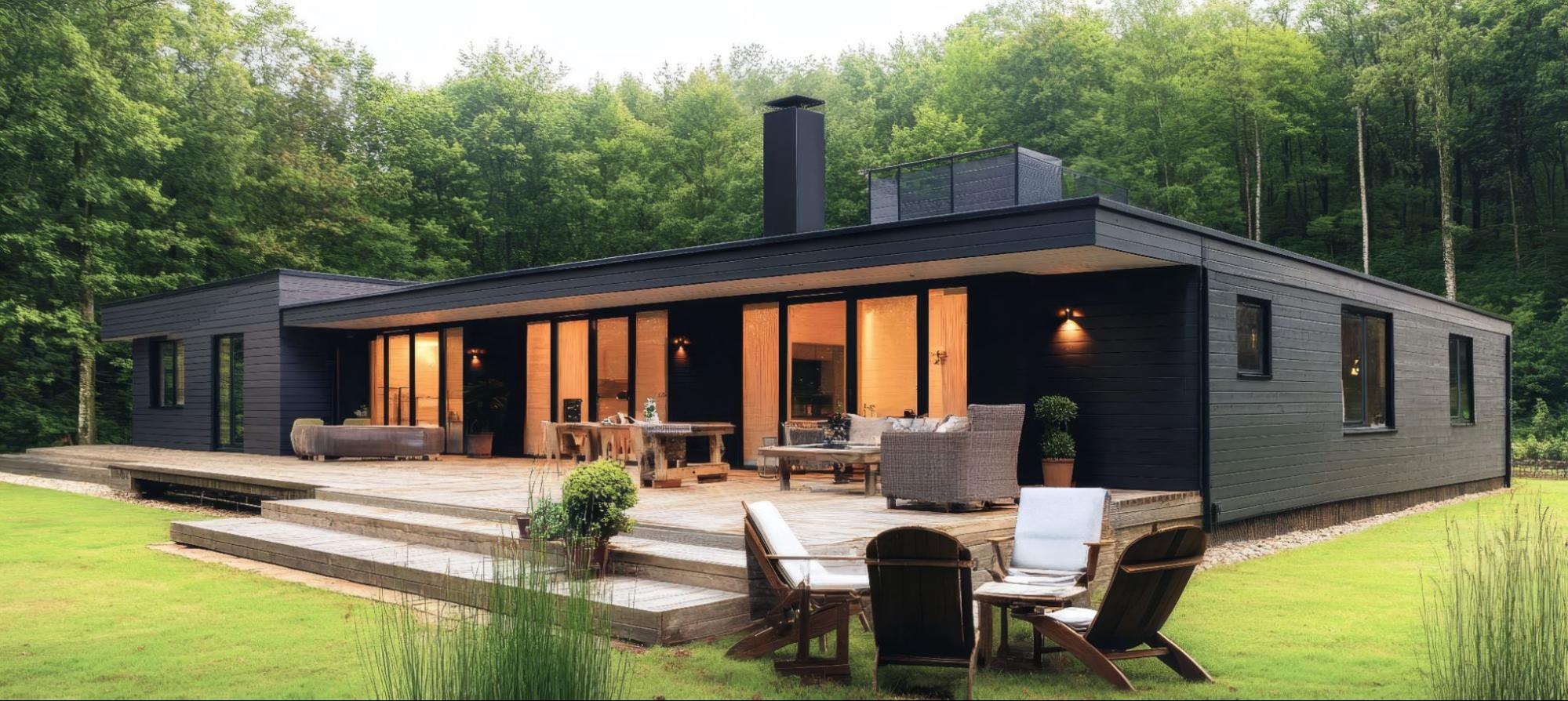

The visual impression your home makes can influence both your enjoyment and its resale value.
Prefab Homes: Without upgrades, panel-built homes can look boxy or utilitarian.
While modern prefab designs can be attractive, achieving a high-end look often requires additional customization or finishes that add to the cost.
Modular Homes: Can be designed to match virtually any architectural style, from modern to traditional, and finished so they are indistinguishable from site-built homes.
Premium siding, roofing, and window options are widely available.
Winner: Modular – offers more flexibility and potential for high-end, customized curb appeal.
10. Structural Performance in Typical Builds
How well a home is built at its core affects both its longevity and safety.
Prefab Homes: Meets required codes, but quality can vary widely depending on the builder and assembly team.
On-site assembly conditions can also influence final strength and performance.
Modular Homes: Built to withstand the stresses of transportation and crane placement, resulting in robust framing and secure joints.
Factory conditions mean consistent quality control across all modules.
Winner: Modular – consistent structural strength and controlled construction give it the edge.
Making Sense of the Results
Modular homes deliver a strong combination of speed, consistent code compliance, durability, curb appeal, and reliable structural quality, making them a solid choice for most homebuyers.
Their ability to match traditional builds in both appearance and value gives them long-term appeal.
Prefab homes hold their own in certain situations, such as remote or challenging sites, projects that may need future expansion, or builds aiming to minimize transport emissions.
Both approaches can achieve high energy efficiency when done well.
For many buyers, modular offers the more balanced mix of performance, aesthetics, and long-term value, while prefab remains a smart alternative for specific needs and site conditions.
Also Read → Mobile Home vs Modular Home: What’s Best for Florida?
Next Steps — Making the Right Choice for Your Next Home Build
Choosing between prefab and modular homes comes down to priorities.
Modular delivers speed, strength, code compliance, and lasting value, while prefab suits unique sites and future flexibility.
Both can perform exceptionally with the right builder and specifications.
Build your modular home with Tri-Town Construction for a hurricane-ready, code-compliant, energy-efficient design that fits your vision and Florida lifestyle.
Our team brings local expertise and proven craftsmanship to every project, ensuring your new home is built to last and ready for anything.
